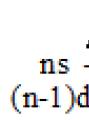Geography
Chemical properties of amines
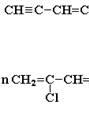
I. By the number of hydrocarbon radicals in the amine molecule: Primary amines R-NH 2 (derivatives of hydrocarbons in which the hydrogen atom is replaced by an amino group -NH 2), Secondary amines R-NH-R "II. By the structure of the hydrocarbon radical: Aliphatic, for example : C 2 H 5
Nanochemistry - Gordon program archive
For the concept of nanotechnology, there is perhaps no exhaustive definition, but by analogy with currently existing microtechnologies, it follows that nanotechnologies are technologies that operate with quantities on the order of a nanometer. Therefore, the transition from “micro” to “nano”
Barium. Properties of barium. Application of barium. What is barium sulfate? How is barium sulfate prepared? Chemical element barium in the periodic table
With the chemical formula BaSO 4. It is an odorless white powder, insoluble in water. Its whiteness and opacity, as well as its high density, determine its main areas of application. History of the name Barium belongs to the alkaline earth metals. P
Hydrogen storage in metals
Inorganic chemistry Joint hydrolysis of salts For example: Problem 1.1. Task 1.2 Answers below Task 1.3. Answers below Reactions of oxides with water For example: Problem 2.1 Mn 2 O 7 + H 2 O = Answers below Problem 3.1 Answers below
Diagonal similarity of elements
chemistry, really necessary! how do the oxidizing properties change in the series of elements S---Se---Te---Po? explain the answer. and received the best answer Answer from Anna Aleksandrovna Tkachenko [active] In the oxygen subgroup, the radius of the atoms increases with increasing atomic number
Chemical methods of analysis
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you. Posted on http://www.allbest.ru/ Introduction 1
Electronic configuration of an atom
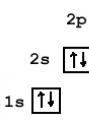
Algorithm for compiling the electronic formula of an element: 1. Determine the number of electrons in an atom using the Periodic Table of Chemical Elements D.I. Mendeleev. 2. Based on the number of the period in which the element is located, determine the number of energy levels;
Feo basic oxide. Iron and its compounds. Chemical formula of iron oxide
DEFINITION Iron (II) oxide under normal conditions is a black powder (Fig. 1), which decomposes upon moderate heating and is formed again from decomposition products upon further heating. After calcination it is chemically inactive. IN
Ammonium nitrates decompose
Nitric acid HNO3 in its pure form is a colorless liquid with a pungent suffocating odor. It is formed in small quantities during lightning discharges and is present in rainwater. Under the influence of light, nitric acid partially decomposes, releasing NO2 and
Grand Duchy of Lithuania in the 14th century Territory of Lithuania in the 14th century
In the XIV-XV centuries. The Grand Duchy of Lithuania and Russia was a real rival of Muscovite Rus' in the struggle for dominance in Eastern Europe. It strengthened under Prince Gediminas (ruled 1316-1341). Russian cultural influence prevailed here at this time. Ge